Main security threats#
Brute force#
Brute force is the action of randomly trying all possible combinations (or word dictionaries) to try to guess a password.
The more complex the password, the more robust it is against brute force.

Fig. 1 Time to brute force a password in 2023 as a function of length and complexity. Credit: Hive Systems with data sourced from https://www.hivesystems.io#
Exemple of hacked passwords#
mt8CIe0Qhh |
eisenach! |
123avier123 |
avier123a12345678910 |
Kraz2kriz |
alaska2. |
12345678910 |
04DI32609 |
ag.53yf |
Kraz2kriz |
firebird14 |
04IE69422 |
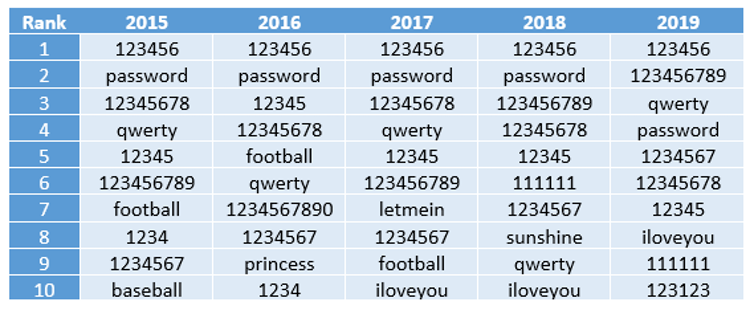
Fig. 2 The 2019 annual SplashData password survey revealed the most common passwords from 2015 to 2019.#

Traffic Interception (http, unsecured Wi-Fi)#
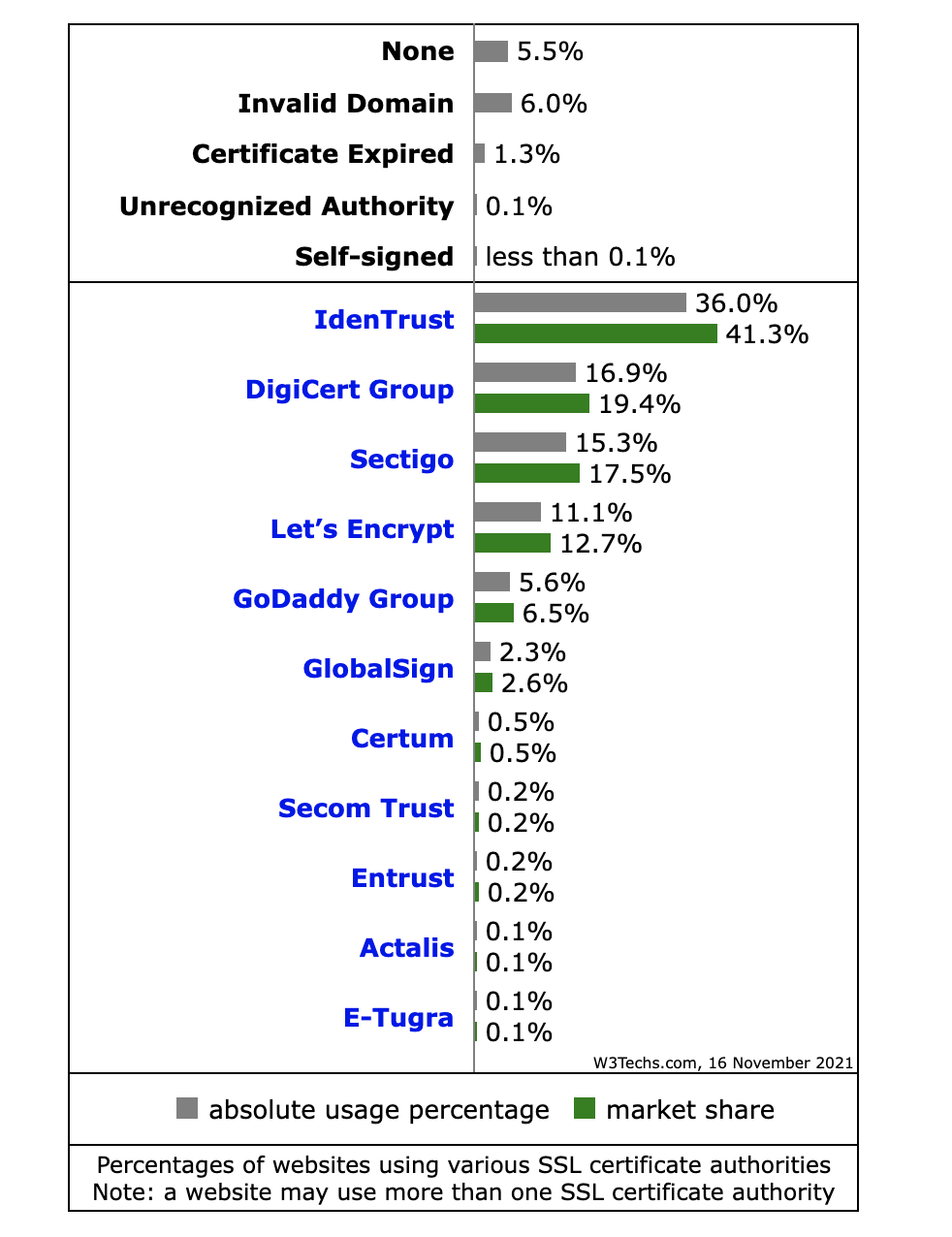
Fig. 3 Percentage of websites using security certificates. Source https://W3techs.com#
Phishing#
Example#
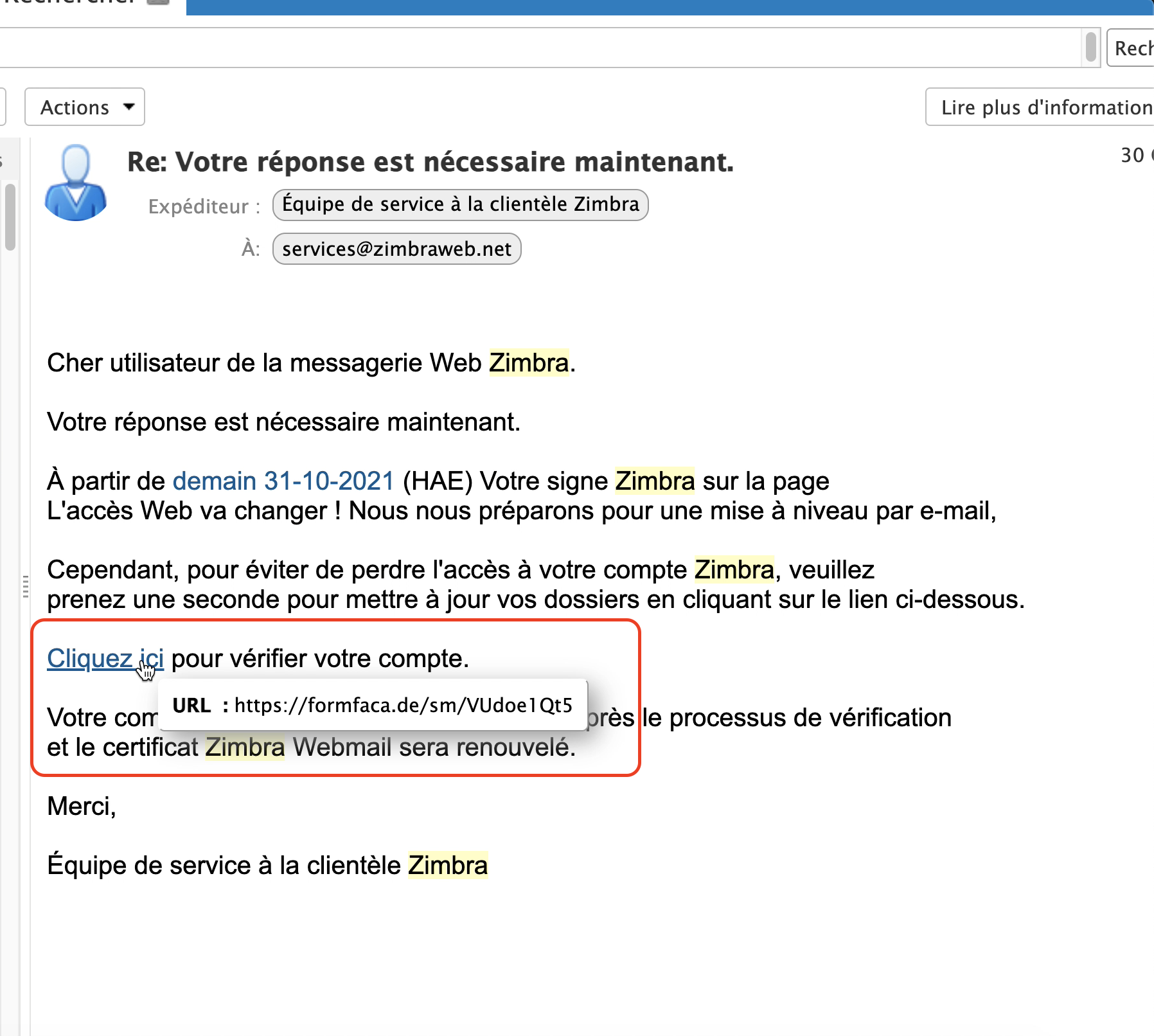
Fig. 4 Always hover over the link to reveal its destination before clicking.#
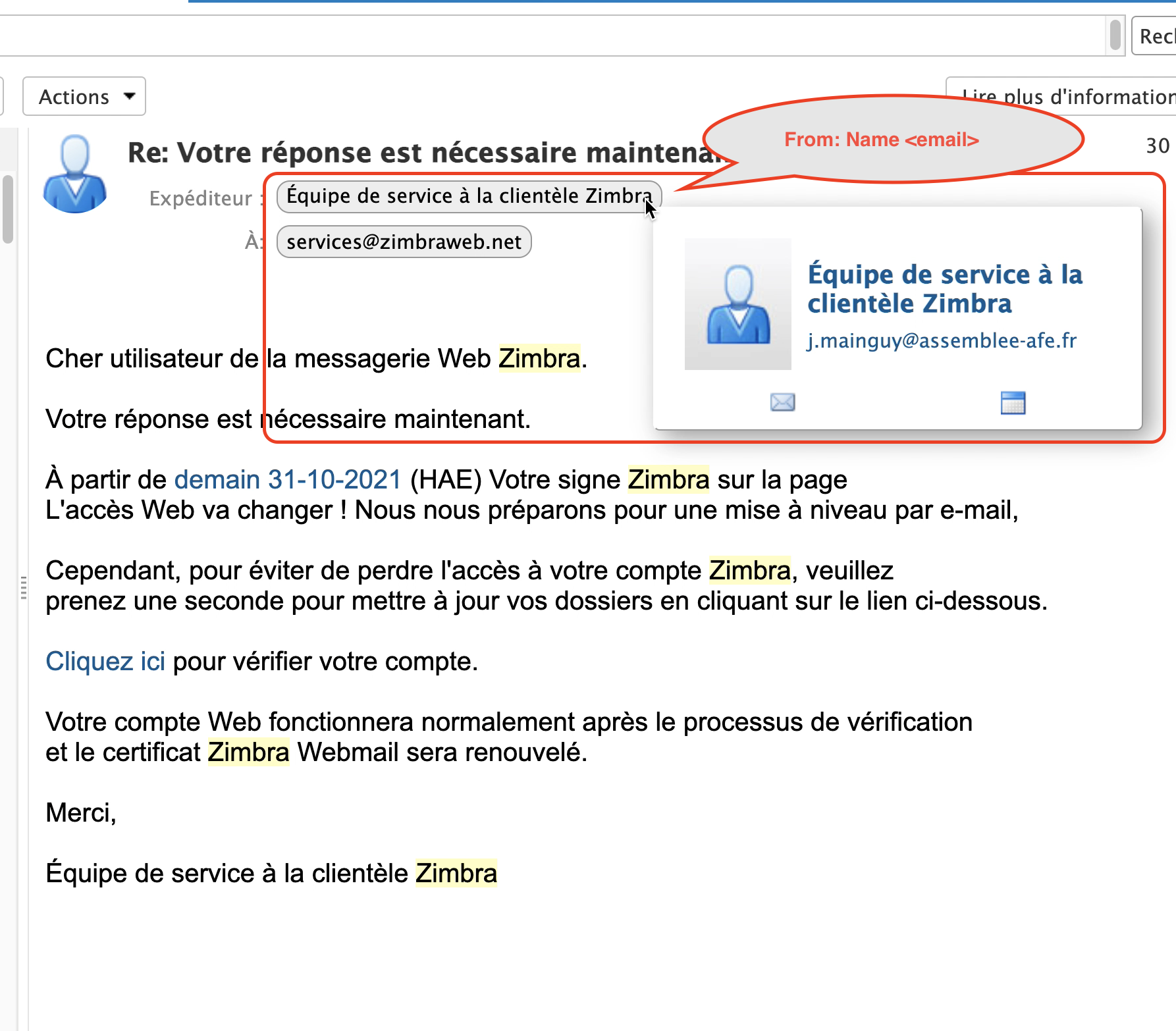
Fig. 5 Check the email address of the sender (not just the displayed name).#
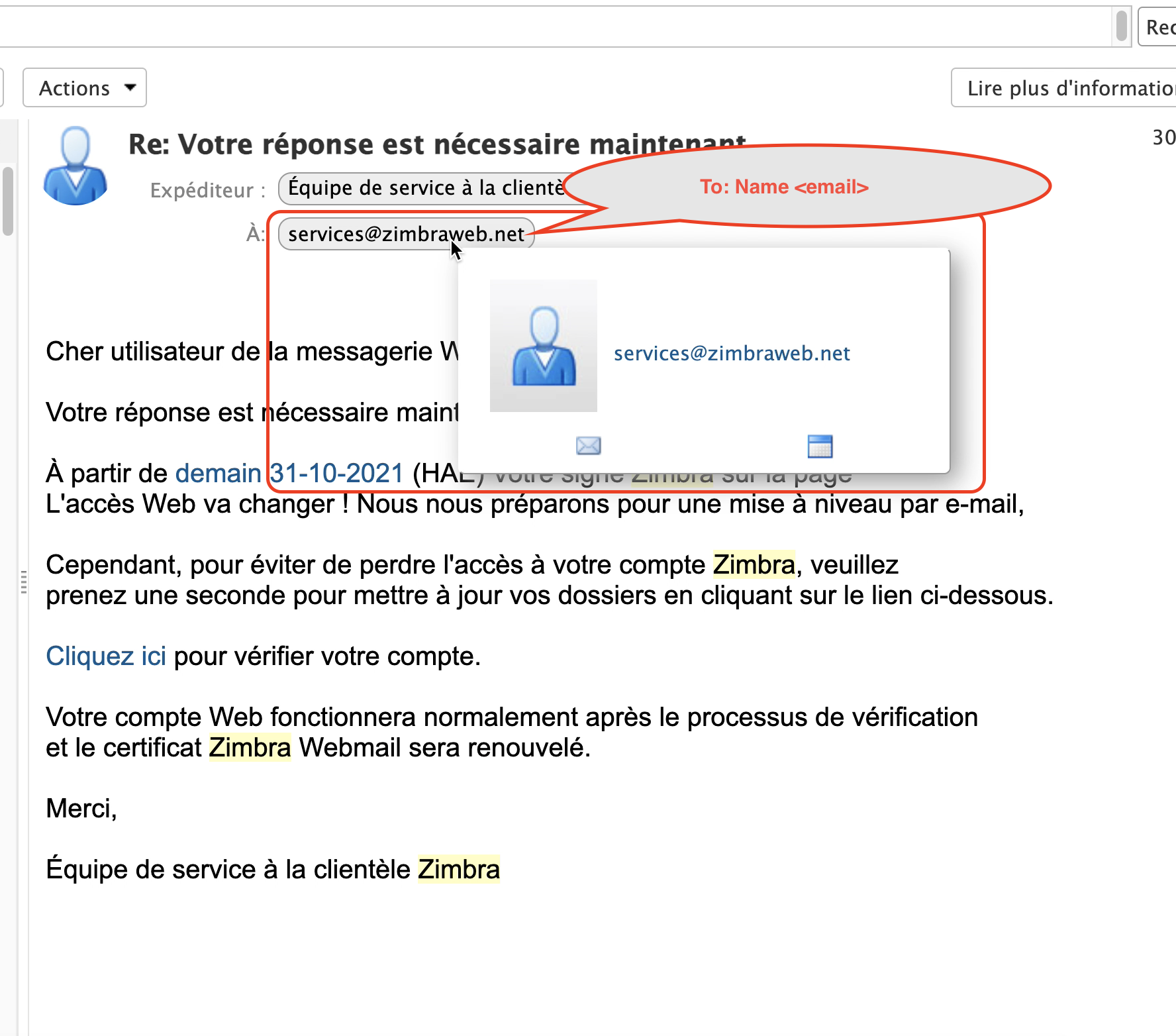
Fig. 6 Also check if the email was sent to you or to lists of people that are totally irrelevant.#
Checking a email header#
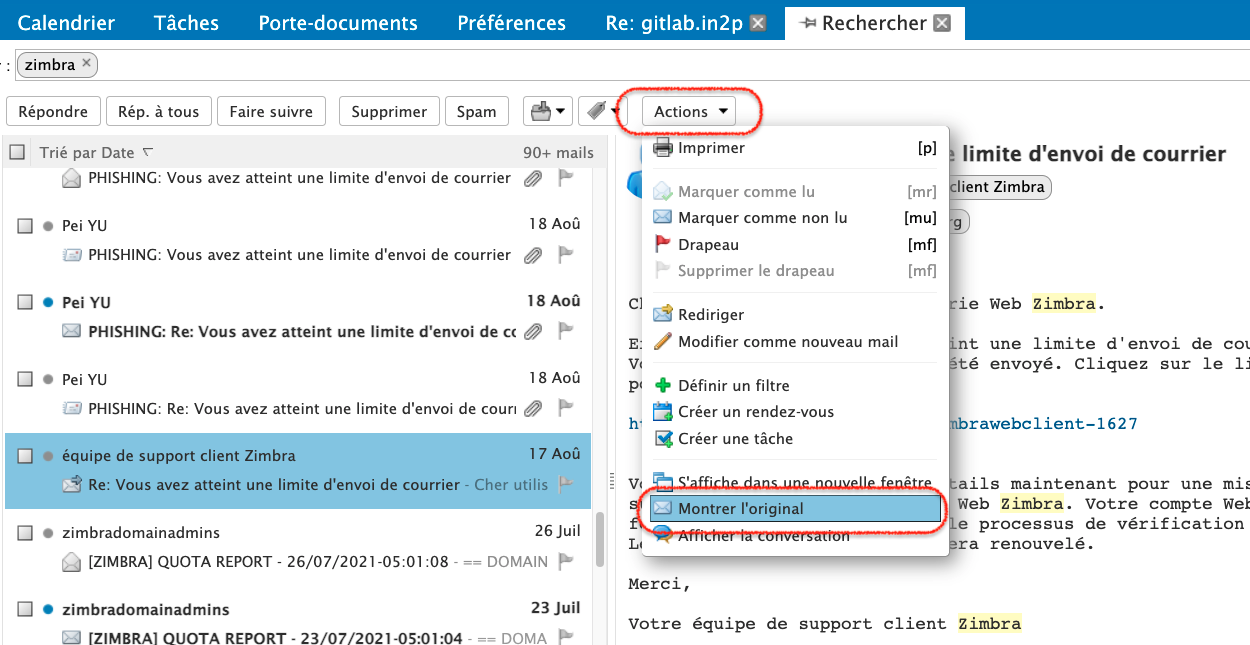
Fig. 7 Show the raw header of an email on the Zimbra webmail.#
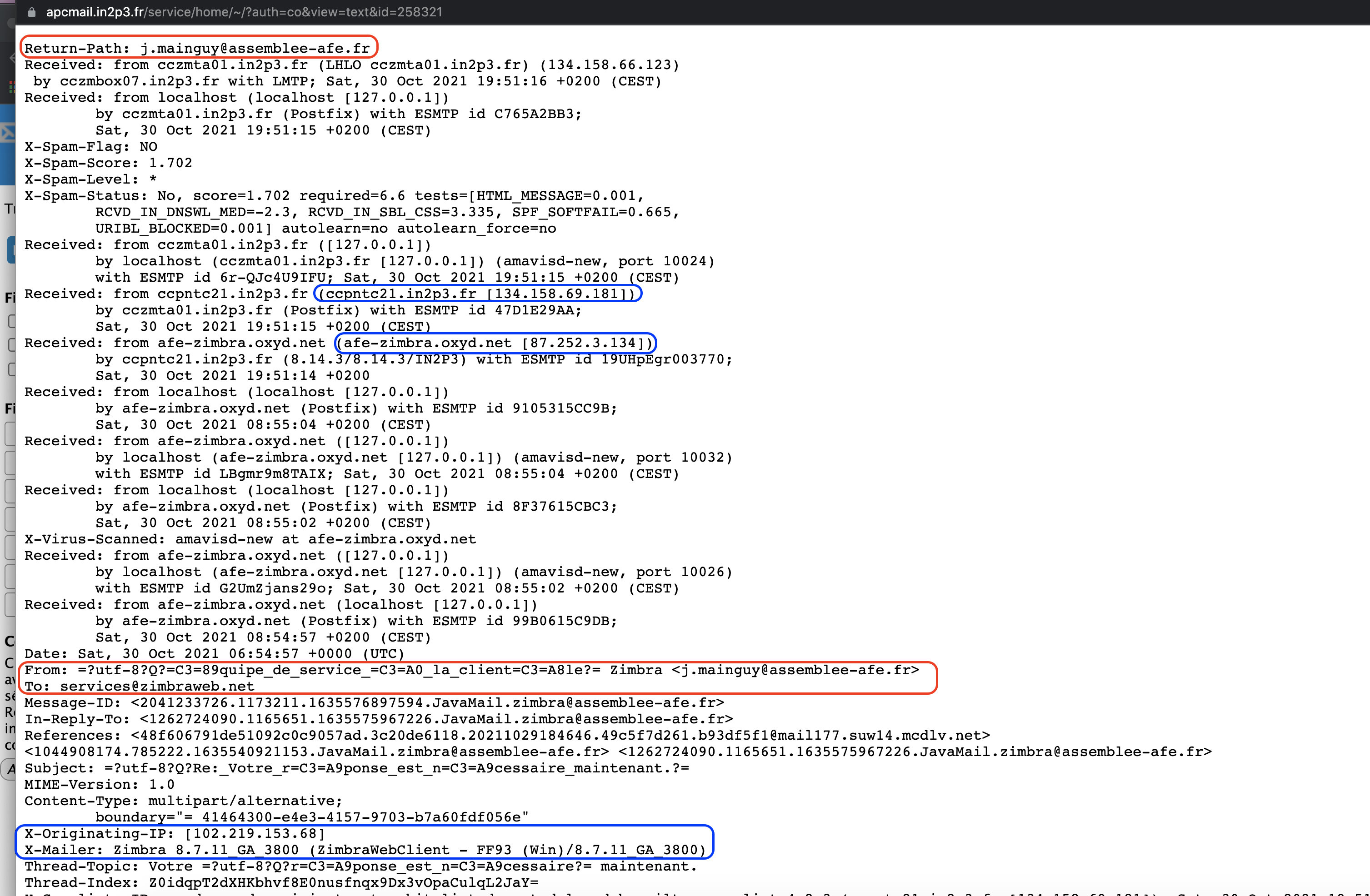
Fig. 8 Carefully inspect the origin of the email.#
Signaling spam#
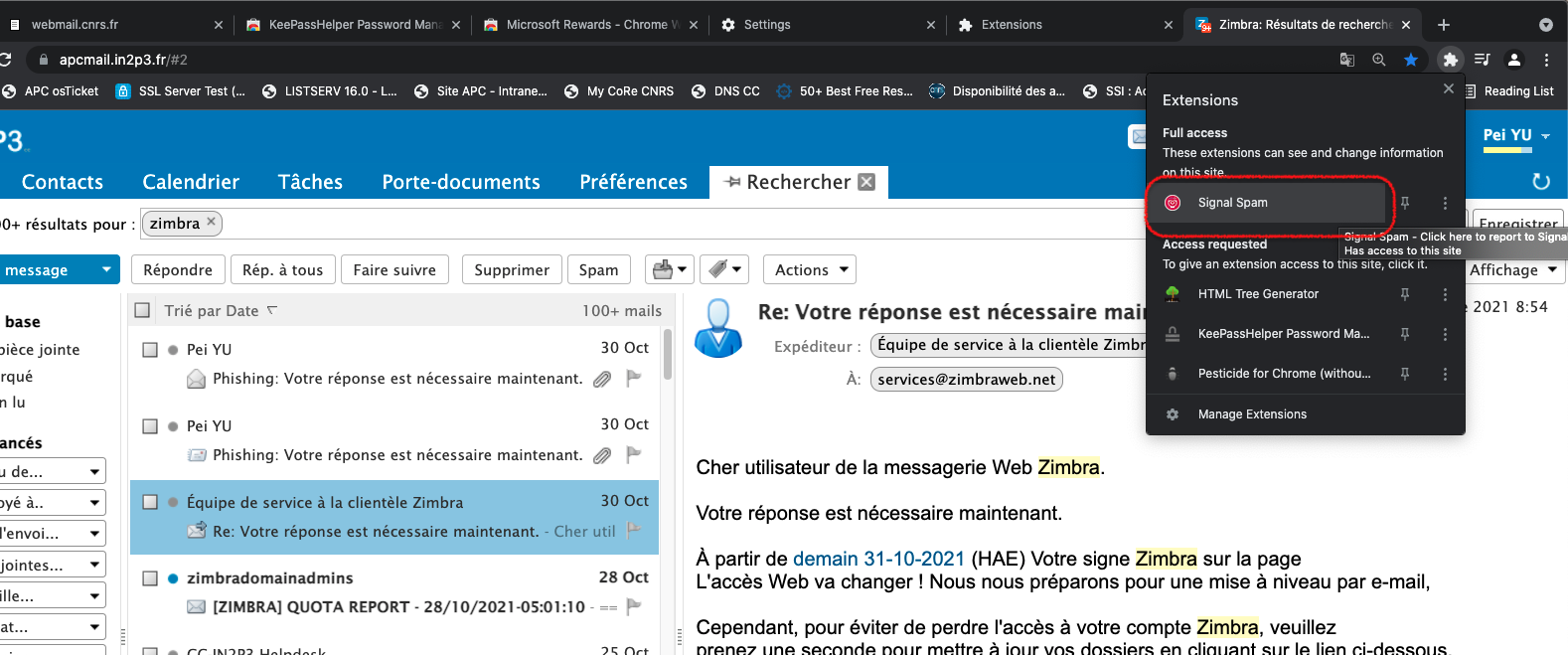
Fig. 9 Take the time to report any malicious emails as spam. This will help the community fight them.#
Mail#
If your APC email is compromised, the attackers will
send a massive amount of SPAM from it => the mail servers of IN2P3 will be blacklisted :(
target email attacks with links or attachments to infect a professional computer => then rebound towards the interior of the IT park to infect more machines and potentially do a lot of harm

Social engineering#
Social engineering is the psychological manipulation of people into performing actions or divulging confidential information.